20
19
Early DecemberThe first COVID-19 patient appeared. The Lancet reported that the first patient developed symptoms on December 1, while the Wuhan Health Commission reported December 8 as the onset date of the first case.
- Epidemic Outbreak
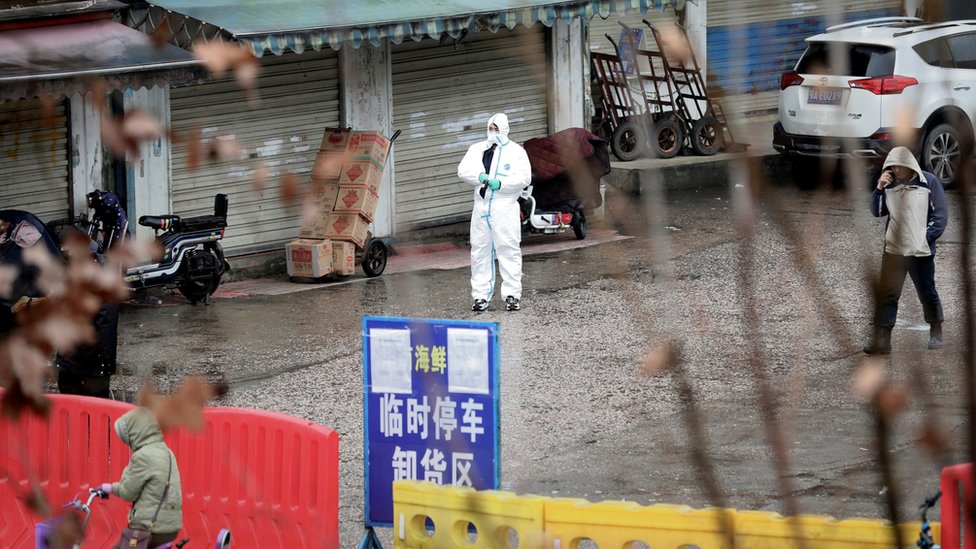
December 30The Wuhan Health Commission issued an internal notice to local medical institutions regarding a "pneumonia of unknown cause." Dr. Li Wenliang blew the whistle in a WeChat group, warning about a coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan.

20
January 1Wuhan police announced that eight people were punished for "spreading rumors" about the outbreak.
January 20Official media confirmed for the first time that the COVID-19 coronavirus was transmissible from person to person.
- Wuhan Lockdown
January 23Wuhan was locked down, followed by gradual lockdowns in other areas of Hubei Province.
- Li Wenliang
February 7Dr. Li Wenliang passed away due to COVID-19.

March 11The WHO declared COVID-19 a global pandemic.
April 8Wuhan officially lifted its lockdown.
- Ruili Lockdown
September 14The city of Ruili on the China-Myanmar border entered its first lockdown, with repeated lockdowns over the next three years.
21
January 1Chinese-made vaccines were rolled out, initiating large-scale vaccination efforts nationwide.
AugustChina's COVID-19 control shifted from regular measures to the "dynamic zero-COVID" approach, emphasizing full-chain and precise control.
- Xi'an Lockdown
DecemberXi'an implemented a lockdown, marking the first use of the term "social dynamic zeroing."
22
- SHANGHAI LOCKDOWN
MarchShanghai began phased lockdowns, with "social dynamic zeroing" replacing "precise control."

- Guizhou Bus Incident
September 18A bus transferring "COVID-related individuals" overturned at night in Guizhou, resulting in 27 deaths.
- Sitong Bridge Protest
October 13Peng Lifa hung banners on the Sitong Bridge in Beijing, protesting lockdowns and dictatorship.
- Tibet Protests
Late OctoberStreet protests broke out in Lhasa, Tibet, over dissatisfaction with COVID lockdown policies.
- Beijing Health Code Pop-ups
October-NovemberBefore the 20th Party Congress, Beijing's health code system caused widespread restrictions on entering the city for two months.
November 11The government issued the "20 Measures," signaling the easing of zero-COVID policies.
- Foxconn Worker Protests
November 22Foxconn workers in Zhengzhou staged large-scale protests against COVID policies and fled the factory en masse.

- Urumqi Fire
November 24A fire in the Jixiangyuan residential complex in Urumqi, Xinjiang, killed 10 people and injured 9, with lockdown measures blamed for hindering rescue efforts.
- White Paper and Other Protests
November 25-27Protests against lockdown policies erupted in universities and streets across different provinces and cities, with blank A4 paper becoming a symbol of dissent.
- Reopening/Great Victory
December 7The central government announced the "New Ten Measures," abruptly ending the zero-COVID policy.
23
February 16The Standing Committee of the Politburo declared a "major decisive victory" in China's fight against COVID-19.